Introduction
It seems to have been much research work carried out on Anxiety and Motivation is foreign countries. But recently on large scale the work is under taken in India on this subject. So such studies are still required in India because of the present poor standard of games and sports hence the researcher has made an earnest to study this problem. Therefore, research scholar felt a need to study the anxiety and motivation level of players and non-players.
There are many dimensions of fear and anxiety in athletes and Non-athletes. Some writers have considered anxiety a personality trait related to stress tolerance in general. Whereas other writers have become interested in "situational anxiety", or fear specific to a given situation or classification of situations.
Numerous steps may be taken to alleviate the anxieties of athletes, depending on a prior assessment of causes of fear in a given participant. For example, an athlete may be told that moderate anxiety and level of activation are helpful to performance and that he or she should not become unduly alarmed by the presence of physiological indices of activation and arousal.
Randhawa (2001) conducted the study of motivational factors in football players in the end it may be concluded that football players of all the categories have been motivated to prefer football game due to their interest that aroused in their childhood. Though other factors have also motivated through out the game, they have been greatly motivated by their interest in the game since their childhood.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
For the purpose of this study the investigator has selected thirty five male players of Basketball, Volleyball and Football each from various Colleges of Punjabi University and has selected thirty five male non-players from various Colleges of Punjabi University. The age of players and non-players was ranging between 17-25 years. The Anxiety scale questionnaire designed by Prof. A. P. Sinha (SCAT) was used, to measure the Anxiety level.
For any response indicated as 'Yes' one score was awarded and any response indicated 'No' was awarded with zero score. The sum of all positive responses was the total Anxiety score of subject.
The Motivation scale questionnaire designed by N.K.M. Tripathi and C.B. Tripathi (A.M.S.) was used for measuring the motivation level.
The students encircled the statement with true or false. For final scoring the key APPROVAL MOTIVE SCALE (AMS) was used.
Results and Discussion
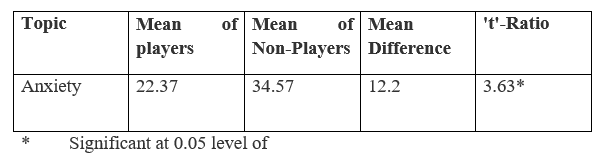
Table 1 presets data regarding mean differences of players and non players on anxiety level between two groups and results shows that there exist statistically significant difference when the whole group of players were compared with .non players (t=3.63> 0.05 level). The comparison of the mean of the two groups indicate that mean of the group of players (x=22.37) was higher then the mean of group of non players (x=35.57) indicating thereby that anxiety level is higher among the non players in comparison to players.
Table No. 1
Table Showing mean difference of Players and Non- Players in Anxiety level
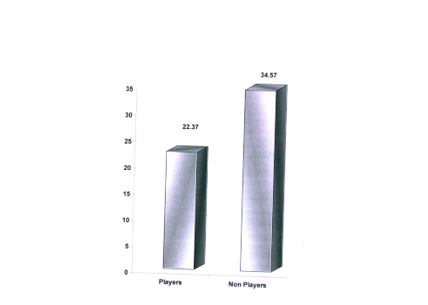
Graph Showing the Mean Difference of Players and Non Players in
Anxiety Level
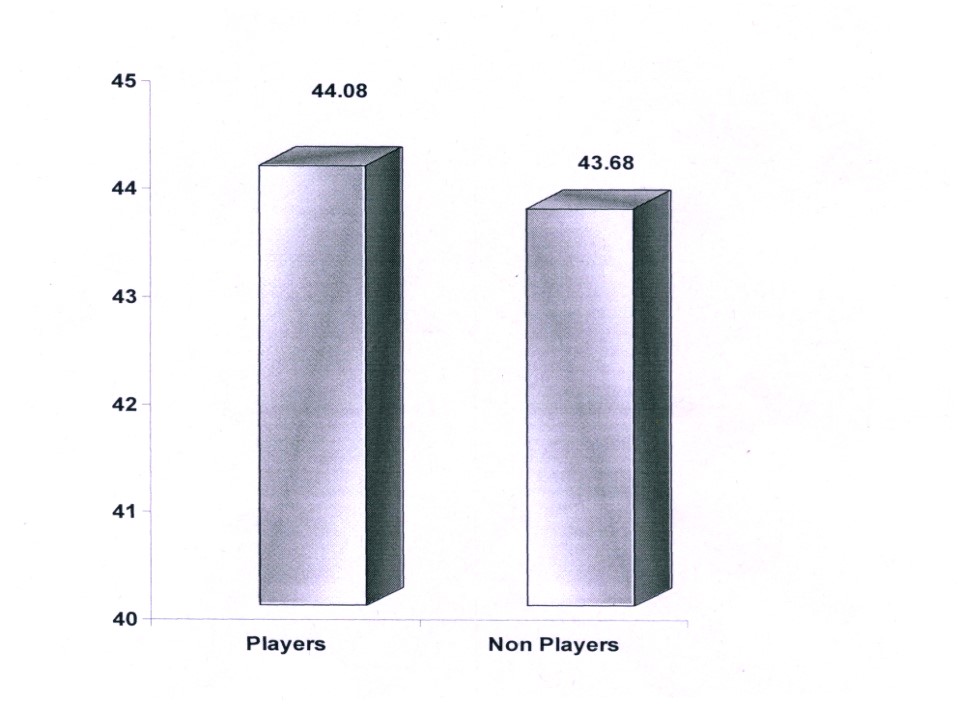
The data tabulated in table 2 regarding motivation level of players and non players reveals that a statistically no significant difference (t=0.02 < 0.05 level) existed when the group of players and non players was compared.


 ©
©