THE IMPACT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS ON THE ENERGY EXPENDITURE OF SECONDARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF CHANDIGARH
Abstract
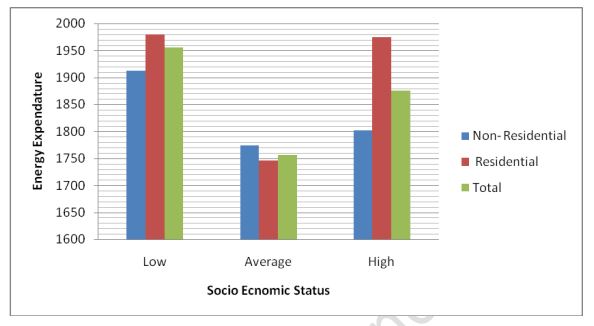
The aim of this study was to assess the energy expenditure of Chandigarh secondary school children according to socio-economic status. 53 children from two different type (residential and non residential) schools were selected for the study. Verma R. P., Prof. P. C. Saxena) 1984 questionnaire was used to collect relevant sociodemographic information. Demographic variables like age, sex, level of education. With this scale three strata wrer formed that is high SES, average SES, and low SES.Energy expenditure was assessed using Bouchards three day physical activity record a 3-day activity record. Every 15-min period over 3 days, including a weekend day, was qualified in terms of energy cost on a 1 to 9 scale corresponding to a range of 1.0 MET to 7.8 METs and higher. Children were classified according to SES out of 53 subjects 49% of students were from low SES, 35% were from average SES and 13% were from high SESit indicate that the majority of were from low SES. Three day Energy expenditure was assessed. Energy expenditure of students ranges from 2649 to 1319kc/kg. Data was analyse, ANOVA2X3 were applied. Low socio-economic status children reported greater levels of average daily energy expenditure (1956.15) but difference is not as much to be significant as compare to other groups, conclusion It was concluded that the neither socio-economic status nor type of school affect the on energy expenditure as no significant difference was found.
Downloads
References
Harold W. Kohl, Janet E. Fulton, and Carl J. Caspersen( 2000). Assessment of Physical Activity among Children and Adolescents: A Review and Synthesis. Preventive Medicine 31, S54– S76
Lazarous, C., Soteriaders, E. S.( 2009). Childrens physical activity T.V Watching and obesity in cyrpus .European journal of public health,20,(1) 70-77 measurement of habitual activity in epidemiological studies. Journal medical & MisraRajiv., Rachel Chatterjee, sujatha, Rao. (2003) Indian health report disease,oxford University press new Delhi 87.Shimai,S. Kamabata, T Niskoka, T Nasski (2000) “ Snaking behaviour among elemantry and junior school students and its relationship to stress copping”. Nippon Kosha Eiser Zarshi 47(1)8-19
Stunkard, A. J & Sobal, J. (1995).Psychological consequences of obesity.In eating disorder and obesity, a comprehensive handbook Ed. The Guildford press new York.
T. W. Odgers. S. C. Langelaan. J. Henzell. C. Chapman (1976) “Energy Expenditure of Grade Four School Children in Western Australia”Australian Journal of Teacher science in sports & exercise ,2
Verma R. P., Saxsena., P. C. Mishra, U. (2008). Manual for socio- economic status index. National psychology cooperation.
Westerterp, K.R.(1999).Assessment of physical activity in relation to obesity current evidence and research issues.J.Med. Sci .sports exercise, 31(11). S522-S525ch, PhD