A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON RESPIRATORY PARAMETERS BETWEEN SHORT DISTANCE AND LONG DISTANCE SWIMMERS
Abstract
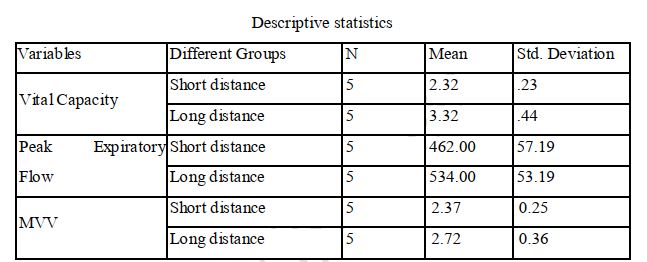
The purpose of the study was to find out the comparison of selected respiratory parameters between short distance and long distance swimmers. The subjects selected for the study was 10 male interuniversity level short distance and long distance swimmers with age ranged between 18-25 years from L.N.I.P.E. Gwalior. The respiratory Parameters Peak Expiratory Flow, Vital Capacity and Maximum Voluntary Ventilation were measured by using Mir Spirometry Pro. To determine the difference in selected respiratory parameters between short distance and long distance swimmers an independent‘t’ test was used. All analyses were performed by SPSS version 20. The mean, S.D,‘t’ test estimated differences between the two groups. The mean and standard deviation of vital capacity of short distance and long distance swimmers were 2.32 ±.23 and 3.32±.44 respectively and for the peak expiratory flow were 462.00±.57.19and 534.00±.53.19 respectively and for maximum voluntary ventilation were 2.37± 0.25and 2.72± 0.36 respectively. The t-value found in relation to respiratory parameters i.e. vital capacity and maximum voluntary ventilation were 4.437and 2.58 respectively. Results revealed that long distances swimmers were found significantly superior in vital capacity and maximum voluntary ventilation as compared to the short distance swimmers, but it was found that there was no significant difference occurred in Peak Expiratory flow variables of short distance and long distance swimmers.
Downloads
References
Astrand and Rodahl Kaare, “Text Book of Work Physiology”, Physiological Basic of Exercise, Singapore, Mc Graw – Hill Book Co., 1986
Joseph P. Winnick, Adapted Physical Education and Sports, Fourth Edition, State University of New York, College at Brockport, 2005, PP 439-441.
Ernest W. Maglischo, Swimming Fastest, Human Kinetics, 2003, PP 703-712
Evelin jaak jurimae, Physiological, biomechanical and anthropometrical predictors of sprint swimming performance in adolescent swimmers journal of sports science and medicine Journal Of Sports Science & Medicine, 2010(9): 398 - 404
Meckel Y, Bishop DJ, The relationship between short- and long-distance swimming performance and repeated sprint ability. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health, 2012 Dec;26(12):3426-31.