EFFECT OF VARIED YOGIC PRACTICES ON RESTING PULSE RATE AND ANXIETY AMONG OBESE MEN
Abstract
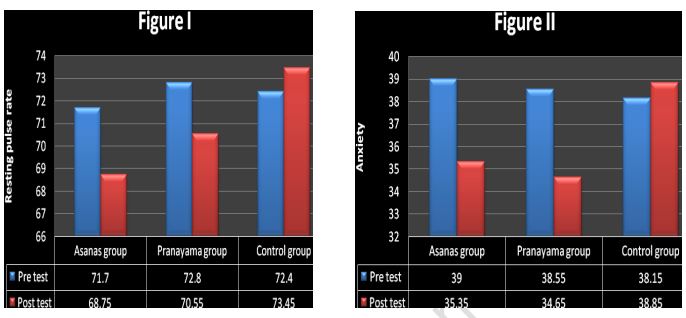
The present investigation was to find out the effects of varied yogic practices on resting pulse rate and anxiety among obese men. 60 obese men age ranges from 25-45 years were selected as participants for the study, from Chennai district, Tamil Nadu. Subjects were divided into two experimental and one control groups of 20 each. Experimental group (I & II) underwent yogic practices for the period of 6 weeks, six days per week for the maximum of an hour in morning. The control group was not exposed to any specific training. The data pertaining to the variables collected from the three groups before and after the training period were statistically analyzed by using Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) to determine the significant difference and tested at 0.05 level of significance. p-value for the F-statistic was 0.00 which was less than 0.05, so of it was significant. , therefore a pair-wise comparison had been made. P-value for the mean difference between Asana group and Control group was 0.00 and Pranayama group and Control group was 0.00, all these p-values were less than 0.05 and hence they were significant at 5% level. Thus, it was concluded that yogic practices can help to decrease the Resting pulse rate and reduced level of Anxiety.
Downloads
References
Bera, T.K., & Rajapurkar, M.V. (1993). Body composition, cardiovascular endurance, and aerobic power of yogic practitioner. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 37(3), 225-228.
Baumgarther. (1975). Measurement for Evaluation in Physical Education, USA: W.B.C Brow Company publication. P.243
Clark, Harison., and Clarke, David H. (1970). Research Processes In Physical Education, Englewood Ciffs, N.J. Prerntic Hall, Inc, P.234.
Clarke, Harrison H. (1976). Application of Measurement to Health and Physical Education, Englewood cliffs, N.J. Prentice Hall Inc., P.169
Joshi, A.R., & Pansare, M.S. (1986). Effect of Yoga Pulmonary Functions Tests. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 30(5), P.9.
Krishnakanthan (1996). Compare the training effects of pranayama and running on selected physiological and psychological variables. Teză de Doctorat înscrisă la Universitatea din Madras.
Kochar, H.C. et al., 1972. Yoga practices as a variable in neuroticism, anxiety and hostility, Yoga Mimansa, 15, PP. 37-46.
Lohan and Rajesh (2002). Effect of asanas and Pranayamas on physical and physiological components of boys between age group 12-16 years. Journal of Adopted Physical Education and Yoga, 7 (2), PP. 47 - 55.
Mohan, Madan (2003). Effect of yoga training on cardioivascular response to exercise and time course of recovery after the exercise. Indian Journal of Physilogical Pharmacology, 35 (2), PP. 201-212.
Mathews, D.K., and Fox, E.L. (1985). The Physiological Basis of Physical Education and Athletics. Philadelphia: W.B.Saunders Co., P. 28.
Oak, J.P., & Bhole, M.V.(1984). Pulse Rate during and after Bhaya Kumbaka with Difference conditi1ons of Abdominal Wall, Yoga Mimamas, 1(22), PP.71-76.
Raju, P.S., Prasad, K.V.V., Venkata, R.Y., Murthy, K.J.R., & Reddy, M.V. (1997). Influence of intensive yoga training on physiological changes in 6 adult women: A case report. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 3(3), 291-295
Ray, U.S., Sinha, B., Tomer, O.S., Pathak, A., Dasgupta, T., & Selvamurthy, W. (2001). Aerobic capacity & perceived exertion after practice of Hatha yogic exercises. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 114, 215-221.
Ramos, Jiménez A., Hernández, Torres RP., Wall, Medrano A., Muñoz, Daw MD., Torres, Durán PV., & Juárez, Oropeza MA.(2009). Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of intensive Hatha Yoga training in middle-aged and older women from northern Mexico. Int. J Yoga. 2, 49–54. [PubMed: 20842264]
Thirumalaisamy. (1997). Statistics in Physical Eduation. Karaikudi: Senthilkumar Publications.
Spielberger, Charles D. (1976). State trait Anxiety Test for Adults, cited in
http://www.mindgarden.com/products/staisad.htm
Verma J P., (2011). Statistical Methods for Sports and Physical Education.Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Ltd.
Weinerb, Eva Lurie. (1984). Anatomy & Physiology, London: Addison Wesley Publishing Company, P.394