ANALYSIS OF JOB STRESS BETWEEN MALE AND FEMALE TEACHERS OF SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL OF GWALIOR
Abstract
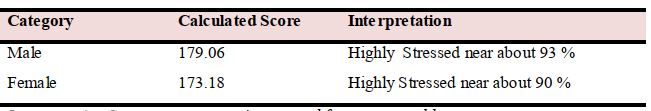
For workers everywhere, the troubled economy may feel like an emotional roller coaster. "Layoffs" and "budget cuts" have become bywords in the workplace, and the result is increased fear, uncertainty, and higher levels of stress. The purpose of the study was to analyze the Job stress of male and female teachers. Selection of subjects: 100 teachers (50 male and 50 female) were randomly selected as subjects of the study from different private senior secondary CBSE schools in Gwalior city of Madhya Pradesh State. The data was collected with the help of Standard Questionnaire. The Collected data was analyzed and interpreted on the objectives of the study with the help of statistical techniques like mean, S.D., Percentile and„t‟ test. The level of significance was set at .05 for comparative statistics. Conclusion: Within the limitations of present study and on the basis of the findings, it was concluded that there is very high degree of Job stress between male and female teachers and male teachers have mo re stress than female teachers. Recommendations: It is recommended that effective measure should be taken by school administration to conduct a good environment in schools so the teachers do not have high level of job stress in their job
Downloads
References
2. D. Fontana, and R. Abouserie “Stress levels, gender and personality factors in teachers” British Journal of Educational Psychology. June 1993;63 : pp. 261-270.
3. Sy Wu, “Study of the intervention measures for the occupational stress to the teachers in the primary and secondary schools” Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. Journal of hygiene health, March 2006; 35:2; p.p. 213-216.
4. http://www.brainyquote.com/quotes/topics/topic_teacher.html#LCpjITJhshCBWrl8.99
5. NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) Publication No. 99- 101taken form http://www.workplace-wellness-massage.com/job-stress-article.html on 1 may 2015
6. Amit Gupta and Rajesh Chandwani, “Job Stress and Performance” an online article taken from http://tejas.iimb.ac.in/articles/24.php on 12 May 2015
7. Jaita Mondal, Sandhya Shrestha, Archana Bhaila, “School Teachers: Job Stress and Job Satisfaction, Kaski, Nepal”, International Journal of Occupational Safety and Health, Vol 1 (2011) 27-33.
8. Cox R. and Brockely D., “The Perception and Outcome of Stress in Teachers.” Journal of Stress and Social Support (1984): P. 143.
9. Gupta S.P., “A Study to Analysis the Causes of Stress among Working Women” Indian Journal of Sports Psychology, July (1982):p. 55.
10. Kawakami N., Haratani T., Kobayashi F., Ishizaki M., Hayashi T., Fujita O., Aizawa Y., Miyazaki S., Hiro H., Masumoto T., Hashimoto S. and Araki S., “Occupational class and exposure to job stressors among employed men and women in Japan” Journal of Epidemiology, Japan Epidemiology Association, November 2004; 14:6; p.p. 204-211
11. Muto S., Muto T., Seo A., Yoshida T., Taoda K and Watanabe M., “Job stressors and job stress among teachers engaged in nursing activity” Journal of Industrial Health Jan 2007; pp. 44-48.