COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF FEMALE CRICKET PLAYERS AT DIFFERENT LEVELS OF PARTICIPATION
Abstract
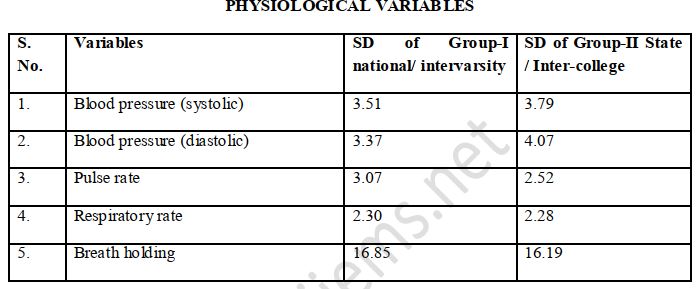
The purpose of the present study was to compare the physiological variables of female cricket players at different levels of participation. The study was administered on 260 women Cricket players in the age group 17-28 years of different levels belonging to Haryana, Punjab and Chandigarh state on the stratified random sampling basis. Physiological variables as blood pressure (diastolic and systolic), pulse rate, breath holding, and respiratory rate were measured. The statistical techniques used to obtain the data were mean, standard deviation, t-test and ANOVA. The findings shows that players of Group-I (Inter-university and national level) are better in blood pressure diastolic, pulse rate, respiratory rate and breath holding from the Group-II (inter-college and state level) women cricket players.
Downloads
References
Jasraj Singh. (1987), "Investigation of selected physiological, psychological anthropome tric variables and functional assessment as predictors of Tennis performance", Unpublished thesis of Doctor of Philosophy, Jiwaji University 1987).
Kamal Saha, "Assessment of Some selected physiological variables as limiting factor in fast bowling in Cricket", Unpublished Master's thesis, Jiwaji University, 1989.
Khanna, G.L. and Manna, I, “Study of Physiological Profile of Indian Boxers” Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2006) 5, 90-98.
Pramanik, P. (2001), "Physical and Physiological Variables as Predictors of P laying Ability of Badminton Players" Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Jiwaji University, Gwalior.
Sodhi H.S. (1998), "P hysiological and Morphological Approach of Athletes and Sportsmen" SNIPES Journal 312 April.
Sodhi, H.S. and L.S. Sidhu (1980), "'Physique and Selection of Sportsmen", Patiala, Punjab Publishing House, 1980, p.146.