PROBLEM SOLVING ABILITY AND ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT AMONG THE STUDENTS BELONGING TO SCHEDULED TRIBE AND SCHEDULED CASTE CATEGORIES
Abstract
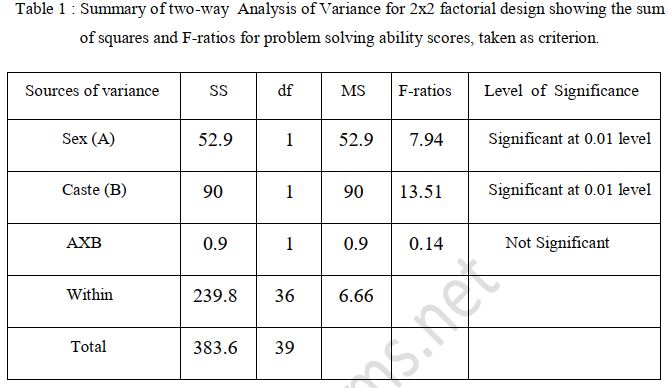
The present study was conducted to ascertain the main and interactional effects of Sex and Caste on the problem solving ability and academic achievement of students. A random sample of 200 students (Boys and Girls) belonging to scheduled tribe and scheduled caste categories was selected from govt. high schools of urban areas of Jammu District. Problem Solving Ability Test prepared and standardized by Dr. L.N. Dubey, Professor Deptt. of Psychology, University of Agra was administered to all of them individually and regarding the academic achievement, the investigator obtained annual examination marks of previous two classes (VIII and IX). The marks were pooled together, added and then percentages found in order to obtain academic achievement index scores of boys and girls belonging to scheduled tribe and scheduled caste categories. The data was analyzed by using two-way analysis of variance technique (ANOVA). The results revealed that Sex and Caste had significant impact on the problem solving ability of students. Sex had no significant impact on the academic achievement of students. Caste had significant impact on the academic achievement of students. However, no interactional effect of sex and caste was found on the problem solving ability and academic achievement of students.
Downloads
References
Chakrabarti, S. (1988). A critical study of intelligence, socio-economic background of the family, educational environment in the family and quality of schools in children of standard V, A case study of some schools in and around Pune, Ph.D. Edu., Pune Univ., in Fourth Survey of Research in Education (1983-88) Vol. I by M.B. Buch NCERT, pp. 350-351.
Chattopadhayay, M.K. (1998). A quasi-experimental study on the educational backwardness of SC secondary school students in some districts of West Bengal, in Sixth Survey of Educational Research (1993-2000) Vol. I NCERT, p. 239.
Kiran, U. (1983). Anxiety, task complexity ans sex as related to verbally expressed preferences and problem solving performance, Ph.D. Psy., Agra U. in Fourth Survey of Research in Education (1983-88) Vol. I by M.B. Buch NCERT, p. 384.
Misra, M. (1986). A critical study of the influence of Socio-economic status on Academic Achievement of Higher Secondary Students in Rural and Urban areas of Kanpur. Ph.D. Edu., Kan. U., in Fourth Survey of Research in Education (1983-88) Vol. I by M.B. Buch NCERT, p. 837.
Narula, K.S. (1979). A Study of Achievement Motivation, Personal Preferences, Perception, Anxiety, Risk-taking behaviour and other Correlates in relation to Intelligence, Socio economic status and Performance of the Prospective Secondary School Teachers of Orissa State. Ph.D. Edu., MSU., in Third Survey of Research in Education (1978-1983) by M.B. Buch NCERT, pp. 385-386.
Rani, B. (1980). Self-Concept and other Non-cognitive Factors affecting the Academic Achievement of the Scheduled Caste students in institutions for Higher Technical Education, in Third Survey of Research in Education (1978-1983) by M.B. Buch NCERT, pp. 682-683.
Shukla, S.K. and Agrawal, Archana (1997). A study of socio-economic status, intelligence, occupational aspiration, self-concept and academic achievement of scheduled castes and non-scheduled castes students, in Sixth Survey of Educational Research (1993-2000) Vol. II. NCERT, p. 396.
Verma, L.K. and Sharma, N.R. (1999). “Advanced Statistics in Educational Psychology”. Narendra Publishing House, Jammu.
Vyas, Uma (1992). A comparative study of the academic achievement of scheduled castes and non-scheduled castes students in relation to self-concept and locus of control. Ph.D. Edu., Agra Univ., in Fifth Survey of Educational Research (1988-1992) Vol. I NCERT. p. 579.