AN 8-WEEK HIGH-INTENSITY INTERVAL TRAINING PROGRAM'S IMPACT ON FEMALE ATHLETES' VITAL CAPACITY
Abstract
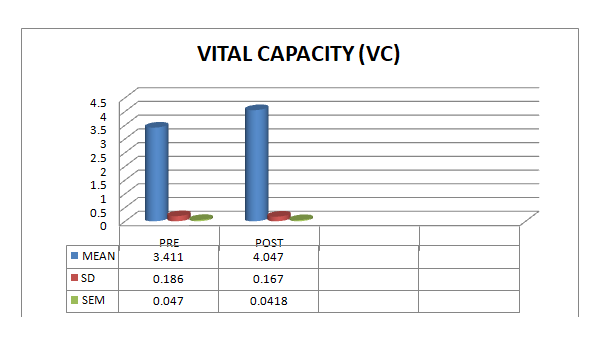
The experimental study was conducted to evaluate the effect of 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training vital capacity of female athletes. The present study was conducted on sixteen (n=16) female athletes from Punjabi University, Patiala. All subjects ranged aged 18-26 were selected in terms of purposive samples under the sampling method of non-probability sampling. The required data were collected through the administration of standardized instruments for the measurement of selected variables. Pre-Test data was collected to measure the primary status of vital capacity before subjects underwent 8 weeks of planned training intervention. Post-Test data was collected after training intervention to evaluate the effect of high-intensity interval training on the vital capacity of female athletes. For analysis and interpretation of data statistical tools were applied e.g., Paired ‘t’, to find out the difference, and compare mean, standard deviation and standard error mean. The result shows that 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training remarkably increase vital capacity in female athletes.
Downloads
References
Bandyopadhyay A. (2015). Validity of Cooper’s 12-minute run test for estimation of maximum oxygen uptake in male university students. Biology of Sport 32(1) 59–63. https://doi.org/10.5604/20831862.1127283
Chhabra S. K. (1998). Forced vital capacity slow vital capacity or inspiratory vital capacity: Which is the best measure of vital capacity? Journal of Asthma 35(4) 361–365. https://doi.org/10.3109/02770909809075669
David S. & Sharma S. (2021). Vital capacity.In StatPearls.StatPearls Publishing. PubMed: 31082143
Gangwar V. John N. A. Verma M. K. John J. Gangwar R. S. &Jasrotia R. B. Impact of moderate and high-intensity exercise on lung volumes lung capacities and breath holding time.
Gething A. D. Passfield L. & Davies B. (2004). The effects of different inspiratory muscle training intensities on exercising heart rate and perceived exertion. European Journal of Applied Physiology 92(1–2) 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1044-2
Hottenrott K. Ludyga S. & Schulze S. (2012). Effects of high-intensity training and continuous endurance training on aerobic capacity and body composition in recreationally active runners. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine 11(3) 483–488
Ketema A. (2020). Effects of high-intensity interval training on physiological variables of university students. Advances in Applied Physiology 5(2) 30–36. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.aap.20200502.14
Singh, M., Kadhim, M.M., Turki Jalil, A. et al. A systematic review of the protective effects of silymarin/silibinin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cancer Cell Int 23, 88 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02936-4 https://cancerci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12935-023-02936-4
Singh, Analysis of set shot in basketball in relation with time to perform the course and displacement of center of gravity, American Journal of Sports Science, Vol.2 Issue.5 pp: 122-126 (2014). Retrieved from https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/paperinfo.aspx?journalid=155&doi=10.11648/j.ajss.20140205.13
Singh (2010). Evaluation And Improvement Of Sports Techniques Through Biomechanical Updated Analyzing Technology, University News, Journal of Higher Education Association of Indian Universities, Association of Indian Universities, Vol:48:Issue.05;2010 Pp45-57, 2010
Mandeep Singh Nathial, A Study of Adjustment and Emotional Intelligence of University Coaches in India, American Journal of Applied Psychology. Volume 3, Issue 6, November 2014 , pp. 122-126. doi: 10.11648/j.ajap.20140306.11
Nathial,. A COMPARATIVE AND ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELF-ESTEEM AND JOB SATISFACTION IN ATHLETES AND NON ATHLETES. Journal of Advances in Social Science and Humanities, 2(10).https://doi.org/10.15520/jassh210123
Singh, M., Kour, R., & Kour, A.,. A collaborative diversified investigation of respective responses of sports person coaches and organizations on criminalization of doping.International Journal of Health Sciences,6(S3), 11295–11310. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS3.8641
Mandeep Singh., Assessment of Vocational Interests of Pahadi&Bakarwal School Students In Relation To Their Gender. Int J Recent Sci Res. 9(3), pp. 24817-24819. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/ijrsr.2018.0903.1731
Dr. Singh, 2017. “A study of awareness of inhouse doping errors among national level players and sports administrators in J&K state of India”, International Journal of Current Research, 9, (01), 45226-45227. http://www.journalcra.com/sites/default/files/issue-pdf/20036.pdf
Singh, 2019; “Effect of Mobile Screen Psychomotor Digital Image Motivators in Person Technique in Reducing Anxiety Level of Intervarsity Players of Cluster University Jammu, Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering and Sciences Publication (BEIESP). Volume-9 Issue-1, October 2019, PP: 3750-3752, DOI: 10.35940/ijeat.A9811.109119. https://www.ijeat.org/portfolio-item/A9811109119/
Singh. (2018). THE AWARENESS OF MOVEMENT AND FITNESS SCIENCES AMONG SCHOOL, UNDER GRADUATE AND POST GRADUATE LEVEL STUDENTS: EMPOWERING EDUCATION THROUGH PHYSICAL EDUCATION. European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science, 4(3).https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1218149
SINGH SIDHU, A., & SINGH, M. (2022). KINEMATICAL ANALYSIS OF HURDLE CLEARANCE TECHNIQUE IN 110M HURDLE RACE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 4(2), 28–35. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/267
Singh, A., & Singh , D. M. (2013). PROMOTION OF RESEARCH CULTURE –ENHANCING QUALITY IN HIGHER EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 2(2), 202–208. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/152
SINGH, M., & SINGH SIDHU, A. (2016). A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BODY COMPOSITION AND RELATIVE HEALTH STATUS AMONG RESIDENT AND NON-RESIDENT STUDENTS IN DIFFERENT SCHOOLS OF J&K. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 5(3), 08–13. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/320
Singh Nathial, D. M. (2012). ANALYZING THE CREDIT BASED SYSTEM IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 1(3), 172–176. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/37
SHARMA, N. P., & SINGH, M. (2014). SENIOR AGE GROUP RELATIVE EXERCISES AND IMPACT ON THEIR LIFESTYLE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 3(04), 78–82. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/246
Laursen P. B. & Jenkins D. G. (2002). The scientific basis for high-intensity interval training: Optimising training programs and maximizing performance in highly trained endurance athletes. Sports Medicine 32(1) 53–73. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232010-00003
Laursen P. B. Shing C. M. Peake J. M. Coombes J. S. & Jenkins D. G. (2005). Influence of high-intensity interval training on adaptations in well-trained cyclists. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 19(3) 527–533. https://doi.org/10.1519/15964.1
Laursen P. B. & Jenkins D. G. (2002). The scientific basis for high-intensity interval training: Optimising training programs and maximizing performance in highly trained endurance athletes. Sports Medicine 32(1) 53–73. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232010-00003
S. Galka, J. Berrell, R. Fezai, L. Shabella, P. Simpson, and L. Thyer, “Accuracy of student paramedics when measuring adult respiratory rate: a pilot study,” Australas. J. Paramed., vol. 16, Apr. 2019, doi: 10.33151/ajp.16.566.
Skow R. J. Day T. A. Fuller J. E. Bruce C. D. &Steinback C. D. (September 2015). The ins and outs of breath holding: Simple demonstrations of complex respiratory physiology. Advances in Physiology Education 39(3) 223–231. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00030.2015
Sporis G. Ruzic L. &Leko G. (2008). The anaerobic endurance of elite soccer players improved after a high-intensity training intervention in the 8-week conditioning program. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 22(2) 559–566.
Tabata I. Nishimura K. Kouzaki M. Hirai Y. Ogita F. Miyachi M. & Yamamoto K. (October 1996). ‘Effects of moderate-intensity endurance and high-intensity intermittent training on anaerobic capacity and?? VO2max’ Med. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 28(10) 1327–1330. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-199610000-00018
Tanisho K. &Hirakawa K. (2009). Training effects on endurance capacity in maximal intermittent exercise: Comparison between continuous and interval training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 23(8) 2405–2410.
Copyright (c) 2023 Rupshikha Deka, Ajay Kumar, Dr. Amarpreet Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














