SPORTS AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: A TOOL TO PROMOTE HEALTH AND PREVENT DISEASE
Abstract
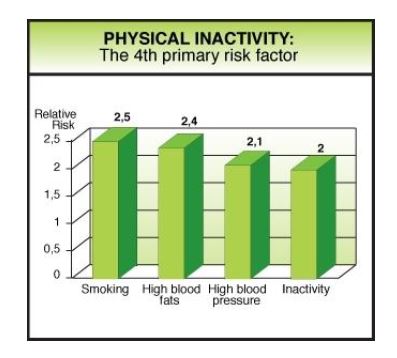
Sports include all forms of physical activity that contribute to physical fitness, mental well-being, and social interaction. Exercise, physical activity, and sport have long been used in the treatment and rehabilitation of communicable and non-communicable diseases. It is a strong means for the prevention of diseases and for nations is a cost-effective method to improve public health across populations. Playing sports can make us live longer, think clearer, react faster, lose weight, and prevent diseases with little to no side effects. It is a compelling medicine that doesn't require a prescription. It explained that activity has beneficial effects on an individual’s health and well-being. Physical activity and sports have positive impact on other major risks, in particular high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, tobacco use, and stress. It reduces morbidity and mortality from mental health disorders. The objective of this paper is to aware people about the importance of sports and physical activity in our life and how they are helpful in controlling and preventing disease. This paper concludes that physical activity reduces the risk of premature mortality in general, and of coronary heart disease, hypertension, colon cancer, and diabetes mellitus in particular. Physical activity also improves mental health and it is important for the health of muscles, bones, and joints. For enhancing sports exercise and physical activity in our routine life so that everybody get fit and active, efforts should be done on increasing physical activity in schools; Help communities keep active; and Promote healthy workplaces.
Downloads
References
Butler RN, Davis R, Lewis CB, et al. Physical fitness: benefits of exercising for the older patient. Geriatrics 53(10):46-62. 1998.
Bouchard, Physical activity and health: introduction to the dose-response symposium. Journal Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 33:S347-350, (2001).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Surveillance Summaries, December 17, 1999. MMWR 48(no.SS-8). 1999.
Health and development through physical activity and sport. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2003.
Hillman CH, Belopolsky AV, Snook EM, Kramer AF, McAuley E. Physical activity and executive control: implications for increased cognitive health during older adulthood. Res Q Exercise Sport. 2004 Jun; 75(2):176-85.
Irish Sports Council (2005) Lifelong Involvement in Sport and Physical Activity: The LISPA Model. Consultation Paper. Dublin: Ireland
CDC. “Physical Activity: Guide to Community Preventive Services.” Accessed from http://www.thecommunityguide.org/pa March 23, 2007.
Powell KE, Pratt M. Physical activity and health. Br Med J 1996; 313: 126–7.
Physical Activity and All-Cause Mortality: What is the Dose Response Relation? Lee, I-Min, Skerrett PJ, (2001) MSSE. Chapter 33, page 6.
“Physical Activity is Fundamental to Preventing Disease “United States Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, 20 June 2002.
Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee (PAGAC). Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Report 2008. Washington, DC, US Department of Health and Human Services, 2008
The significance of sport for society: health, socialization, economy; Vuori I., Fentem P. Strasbourg Cedex: Council of Europe, 1995
WHO, the World Health Report 2002: Reducing risks, promoting healthy life. 2002, World Health Organization: Geneva.