RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOTOR ABILITIES AND CLEAR SKILLS OF BADMINTON PLAYERS
Abstract
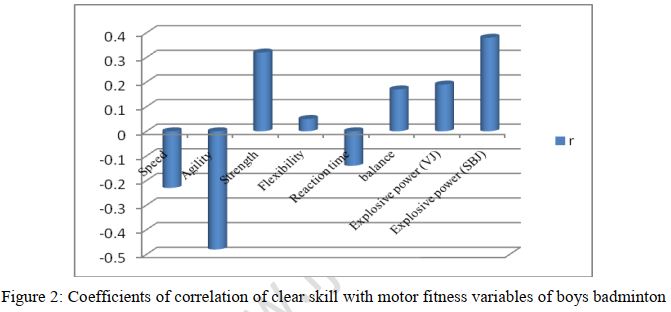
The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between motor abilities and clear skill of badminton players. Methodology: 60 badminton players (40 boys and 20girls) were selected from various badminton coaching centers of Chandigarh having age ranged from 13 to 16 years. Motor abilities namely agility, balance, flexibility, explosive power (SBJ&VJ), reaction time, speed, strength were measured by conducting 10 yards shuttle run, Stork balance, bend and reach, standing broad jump (SBJ), Sargent jump(VJ), Nelson hand reaction, 30 meter dash, situp tests. Hicks clear skill test were used to assess the badminton skill of the selected subjects. Pearson Product moment coefficient of correlation with significant level at (p<0.05) was used to examine the correlations between clear skill and agility, balance, flexibility, explosive power, reaction time, speed, strength. Result The findings revealed that in boys badminton players clear skill ability was positively significantly correlated with the strength (r = 0.32), (SBJ) explosive power (r = 0.38), and negatively correlated with the agility(r = -0.48). However it was not significantly correlated with speed, flexibility, reaction time, balance and explosive power (VJ) of boys badminton players. In case of girls badminton players the results indicated that the clear skill was positively correlated with flexibility (r = 0.48), (SBJ&VJ) explosive power (r = 0.53 and 0.54), and negatively correlated with the speed (r = -0.48), agility(r = -0.62). But it was not significantly correlated with strength, reaction time, and balance ability of girls badminton players.
Downloads
References
Chi, S. C. (1996). The study of a specific badminton physical fitness test on badminton singles players. Journal of physical education and sports, 6(2), 63-81.
Downey, J. & Boride, D. (1982). Get fit for Badminton. (London: Pelham Books Ltd.,), 18, 20 &160
Johnson, B. L, Nelson, J. K. (1979). Practical measurements for evaluation in physical education. 4th edition. Minneapolis: Burgess.
Lieshout, K. A. V., & Lombard, A. J. J. (2003). Physiological profile of elite junior badminton players in South Africa. African Journal for Physical, Health Education, Recreation and Dance, 9(3), 114-120.
Pinto, M. J. (1982). “Badminton Indian” (Official publication of BAI), p.12.
Raza, S. (2008). Relationship of Selected Physical Variables with the Performance of Badminton Players. Source: http://www.shvoong.com/humanities/
Scott, G. & French, E. (1959). Measurement and evaluation in physical education. W.M.C. Brown Company Publishers, Dubuque Lowa.
Whetnall, P. & Morris, R. (1981). An introduction to badminton. Video Sports for All in association with Astral Sports and Leisure. Badminton association of England