THE IMPACT OF EIGHT WEEKS OF PLYOMETRIC TRAINING ON AGILITY ENHANCEMENT IN MALE BASKETBALL PLAYERS: A SCIENTIFIC EXPLORATION
Abstract
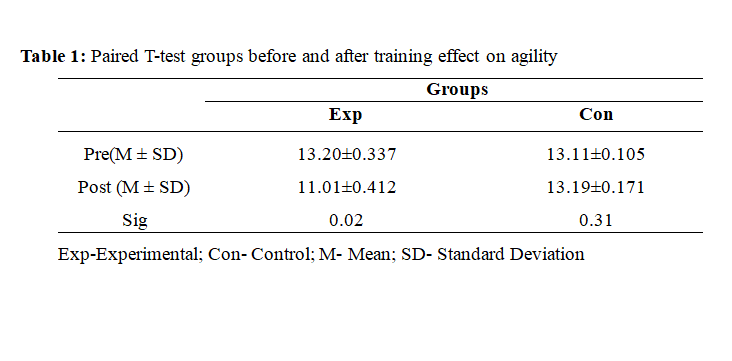
This research study aimed to assess the effects of an eight-week plyometric training program on the agility of male basketball players. A total of thirty male basketball players were randomly selected from the Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India, for participation in this study. These participants were divided equally into two groups: the plyometric training group (n=20) and the control group (n=20). The plyometric training group engaged in a twice-weekly training regimen over the course of eight weeks, focusing on plyometric exercises, while the control group did not partake in any specialized training. To evaluate the impact of the training program, a specific agility test known as the T-test was employed before and after the eight-week period for both groups. The collected data were subjected to statistical analysis using Paired T-test to determine any significant differences. The results indicated that the experimental group shows significantdifference between pre and post-test on agility improvement (p<0.05), with the plyometric training and enhancement in agility performance. In conclusion, this study provides evidence that an eight-week plyometric training intervention can significantly enhance the agility of male basketball players. The findings underscore the effectiveness of plyometric training as a targeted method for improving agility in athletes. Incorporating plyometric exercises into training programs could yield valuable results for coaches, trainers, and athletes seeking to enhance performance in sports that demand quick changes in direction and rapid movements. Further research could explore the long-term effects of such training on agility and its applicability to other sports or athletic populations.
Downloads
References
J. M. Sheppard, W. B. Young, Agility literature review: Classifications, training and testing, Journal of Sports Sciences, 24 (2006) 919-932.
J. L. Barnes, B. K. Shilling, M. J. Falvo, L. W. Weiss, A. K. Creasy, A.C. Fry, Relationship of jumping and agility performance in female volleyball athletes, Journal of Strength and Conditioning research, 21 (2007) 1192-1196.
L. S. Parsons, M. T. Jones, Development of speed, quickness and agility for tennis athletes, Strength and Conditioning Journal, 20 (1998) 14– 19.
D. A. Chu (1998) Jumping into Plyometrics, 2nd Ed, Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
M. G. Miller, D. C. Berry, S. Bullard,R. Gilders, Comparisons of land-based and aquatic based plyometric programs during an 8-week training period, Journal of Sports Rehabilitation, 11 (2002) 268-283.
M. G. Miller, J. J. Herniman, M. D. Ricard, C. C. Cheatham, T. J. Michael, The effects of a six-week plyometric training program on agility, Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 5 (2006) 459-465.
C. W. Yap, L. E. Brown, Development of speed, agility, and quickness for the female soccer athlete, Strength and Conditioning, 22 (2000) 9-12.
W. B. Young, M. H. McDowell, B. J. Scarlett, Specificity of spring and agility training methods, Journal ofStrength and Conditioning Research, 15 (2001) 315-319.
M. L. Stane, M. E. Powers, the effects of plyometric training on selected measures of leg strength and power when compared to weight training and combination weight and ploymetric training, Journal of Athletic Training, 42 (2005)186- 192.
Mandeep Singh Nathial, A Study of Adjustment and Emotional Intelligence of University Coaches in India, American Journal of Applied Psychology. Volume 3, Issue 6, November 2014 , pp. 122-126. doi: 10.11648/j.ajap.20140306.11
Singh, 2017. “A study of awareness of inhouse doping errors among national level players and sports administrators in J&K state of India”, International Journal of Current Research, 9, (01), 45226-45227. http://www.journalcra.com/sites/default/files/issue-pdf/20036.pdf
J N Baliya, 2013; “A study of family stress among working and non-working parents”, International Journal of Research in Social Sciences.Vol 2, 2. 194-201. https://indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijrss&volume=2&issue=2&article=013
Singh, 2019; “Effect of Mobile Screen Psychomotor Digital Image Motivators in Person Technique in Reducing Anxiety Level of Intervarsity Players of Cluster University Jammu, Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering and Sciences Publication (BEIESP). Volume-9 Issue-1, October 2019, PP: 3750-3752, DOI: 10.35940/ijeat.A9811.109119. https://www.ijeat.org/portfolio-item/A9811109119/
B. M. Robinson, B. Owens, Five-week program to increase agility, speed, and power in the preparation phase of a yearly training plan, Strength and Conditioning, 26 (2004) 30-35.
W. B. Young, M. H. McDowell,B. J. Scarlett, Specificity of sprint and agility training methods, Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 15 (2001) 315-319.
M. Alricsson, K. H. Ringdahl, S. Werner, Reliability of sports related functional tests with emphasis on speed and agility in young athletes, Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 11 (2001) 229-232.
W. P. Ebben, Complex training: A brief review, Journal of Sports Science and Medicine, 1 (2002) 42-46.
SINGH, M., & SINGH SIDHU, A. (2016). A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BODY COMPOSITION AND RELATIVE HEALTH STATUS AMONG RESIDENT AND NON-RESIDENT STUDENTS IN DIFFERENT SCHOOLS OF J&K. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 5(3), 08–13. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/320
Singh Nathial, D. M. (2012). ANALYZING THE CREDIT BASED SYSTEM IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 1(3), 172–176. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/37
SHARMA, N. P., & SINGH, M. (2014). SENIOR AGE GROUP RELATIVE EXERCISES AND IMPACT ON THEIR LIFESTYLE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 3(04), 78–82. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/246
B. S. Bal, P. J. Kaur, D. Singh, Effects of a short term plyometric training program of agility in young basketball players, Brazilian Journal of Biomotricity, 5 (2011) 271-278.
Copyright (c) 2019 Chetna Chaudhary

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














