EMOTIONAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH OF PUNJAB POLICE WOMEN CONSTABLES
Abstract
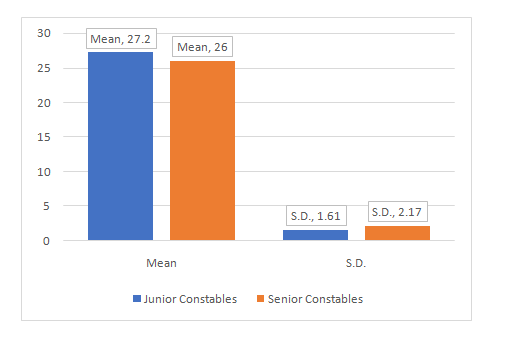
Aim of study: The aim of this study was to assess the status of emotional health & environmental health status among Punjab Police women constables. Material and Methods: A sample of Thirty(N=30) women constables from Punjab Police has been selected randomly and further bifurcated into two classes i.e., N1: Junior Constables with experience up to 1 year and N2: the Constables with the job up to 10 years Senior Constables, for the in-depth analysis. The tool used for data collection was a structured ‘Wellness Questionnaire’ which was constructed by Gordon Edlin and Eric Golanty in 2004. The mean, S.D. and ‘t-test’ were calculated to find out the significance of difference between the groups. Results: mean and S.D. of Junior and Senior Punjab Police Women Constables for their emotional health status variable is 27.20 ± 1.61 and 26.00 ± 2.17 respectively and Environmental Health variable is 28.46 +- 1.55 and 29.20 +- 1.65 respectively. The calculating ‘t’-value (1.718), of emotional health status which is less than the tabulated ‘t’-value (2.048), at 0.05 level. So, it shows that there is an insignificant difference between Junior and Senior Punjab Police Women Constables for their Emotional Health Variable. The calculated ‘t’-value (1.251), Environmental Health Variable which is more than the tabulated ‘t’-value (2.048) at 0.05 level. So, it indicates that there is a insignificant difference between Junior and Senior Punjab Police Women Constables for their Environmental Health Variable.
Downloads
References
Balog, J.E. (1981). The concept of health and the role of health education. The Journal of School Health, 9, 462-464.
CHAND PURI, P., MISHRA, P., JHAJHARIA, B., & SINGH, M. (2014). COORDINATIVE ABILITIES OF VOLLEYBALL IN DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 3(3), 56–68. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/228
Chandler, C. K., Holden, J. M., & Kolander, C. A. (1999). Counseling for spiritual wellness: Theory and practice. Journal of Counseling and Development, 71, 168-175.
Edlin, G., & Golanty, E. (2015). Health and wellness (13th Ed.). Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Gul, Z., & Delice, M. (2011a). Police job stress and stress reduction/coping programs: the effects on the relationship with spouses. Turk J Police Stud, 13, 19–38.
Mandeep Singh Nathial, Analysis of set shot in basketball in relation with time to perform the course and displacement of center of gravity, American Journal of Sports Science, Vol.2 Issue.5 pp: 122-126 (2014). Retrieved from https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/paperinfo.aspx?journalid=155&doi=10.11648/j.ajss.20140205.13
Mandeep Singh (2010). Evaluation And Improvement Of Sports Techniques Through Biomechanical Updated Analyzing Technology, University News, Journal of Higher Education Association of Indian Universities, Association of Indian Universities, Vol:48:Issue.05;2010 Pp45-57, 2010
Mandeep Singh Nathial, A Study of Adjustment and Emotional Intelligence of University Coaches in India, American Journal of Applied Psychology. Volume 3, Issue 6, November 2014 , pp. 122-126. doi: 10.11648/j.ajap.20140306.11
Nathial, Mandeep Singh. A COMPARATIVE AND ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELF-ESTEEM AND JOB SATISFACTION IN ATHLETES AND NON ATHLETES. Journal of Advances in Social Science and Humanities, 2(10).https://doi.org/10.15520/jassh210123
Andrew, L. (1999, November 22). Wellness promotion: A people ready strategy. The Barbados Advocate, Business Monday, pp. 6-7.
World Health Organization. Strengthening Mental Health Promotion. Geneva, World Health (Fact sheet no. 220), 2001.
Parsons, J. R. (2004). 'Occupational Health and Safety Issues of Police Officers in Canada, the United States and Europe: A Review Essay'.
Reddy, S. (2008). Employee Health and Wellness Programs – Perspectives and Cases – pp 106-107.
SINGH SIDHU, A., & SINGH, M. (2022). KINEMATICAL ANALYSIS OF HURDLE CLEARANCE TECHNIQUE IN 110M HURDLE RACE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 4(2), 28–35. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/267
Singh, A., & Singh , D. M. (2013). PROMOTION OF RESEARCH CULTURE –ENHANCING QUALITY IN HIGHER EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 2(2), 202–208. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/152
SINGH, M., & SINGH SIDHU, A. (2016). A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BODY COMPOSITION AND RELATIVE HEALTH STATUS AMONG RESIDENT AND NON-RESIDENT STUDENTS IN DIFFERENT SCHOOLS OF J&K. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 5(3), 08–13. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/320
Singh Nathial, D. M. (2012). ANALYZING THE CREDIT BASED SYSTEM IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 1(3), 172–176. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/37
SHARMA, N. P., & SINGH, M. (2014). SENIOR AGE GROUP RELATIVE EXERCISES AND IMPACT ON THEIR LIFESTYLE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 3(04), 78–82. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/246
Sharma, A., & Verma, S. (2019). Status of health and wellness among Chandigarh police male constables.
Singh, G., & Singh, A. (2018). Comparative study of fitness and body care status between teaching and non-teaching employees of Punjabi university Patiala.
Copyright (c) 2023 Yadwinder Kaur, Bakhsis Singh, Amarpreet Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














