AN INVESTIGATION BETWEEN RECOVERY INTERVENTIONS OF SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE
Abstract
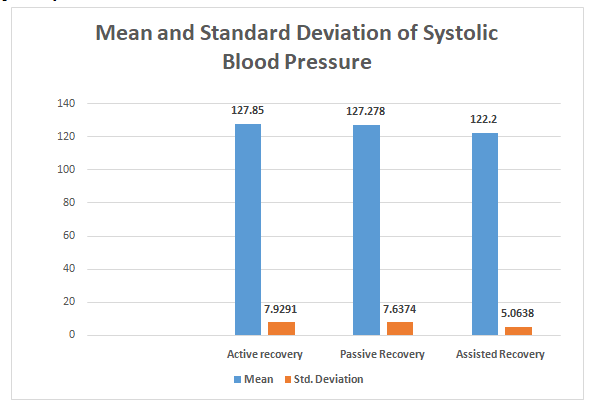
The presented study was to identify the recovery treatment difference of active recovery, passive recovery and assisted recovery on systolic blood pressure. In this study there are total 58 subjects were taken (20 active recovery, 18 passive recovery and assisted recovery 20 male) all were national player of middle distance runners from Bhopal SAI centre. Their age ranging from 18 to 25 years. The data were assessed through blood pressure monitor. The collected data was analysed by computing the descriptive statistics to find out standard deviation and mean among active, passive and assisted recovery on systolic blood pressure, one way -ANOVA and the Multiple ComparisonsScheffe post hoc. Test. For testing the hypothesis, the degree of significance was set at 0.05. Statistical analysis was conducted by using statistical packages for social science (IBM SPSS 20 Version). As a result the findings state that the value of f-statistics is having significant difference among active and assisted recovery (3.932, p<0.05) because P value is smaller than 0.05. Thus the null hypothesis is fail to accept and the study concluded that there is no significant difference among active and passive recovery due to p-value is greater than 0.05 but there is a significant difference between active recovery and assisted recovery. Which interpret that active and passive recovery does not have significant difference and there is a slight difference between active and assisted recovery in regard of systolic blood pressure so, assisted recovery helps to down the systolic blood pressure after an exercise or workout.
Downloads
References
Andriana, L. M., Sundari, L. P. R., Muliarta, I. M., Ashadi, K., & Nurdianto, A. R. (2022). Active recovery is better than passive recovery to optimizing post-exercise body recovery. Jurnal SPORTIF: Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran, 8(1), 59-80.
Brown, S. P., Clemons, J. M., He, Q., & Liu, S. U. (1994). Effects of resistance exercise and cycling on recovery blood pressure. Journal of sports sciences, 12(5), 463-468.
Dimkpa, U., & Ugwu, A. C. (2008). Age-related differences in systolic blood pressure recovery after a maximal-effort exercise test in non-athletic adults. International journal of exercise science, 1(4), 142.
Dimkpa, U., & Ugwu, A. C. (2009). Determination of systolic blood pressure recovery time after exercise in apparently healthy, normotensive, non-athletic adults and the effects of age, gender, and exercise intensity. International journal of exercise science, 2(2), 5.
Dr.Mandeep Singh & J N Baliya, 2013; “A study of family stress among working and non-working parents”, International Journal of Research in Social Sciences.Vol 2, 2. 194-201.
Gayatri, P., & Kumar, D. P. (2015). Effects of active and passive recovery on selected physiological variables among hockey players. Scholarly research journal for interdisciplinary studies, 3(18), 15-25.
Guru, K., Gourang, S. A., & Singh, S. J. (2013). Effect of active arm exercise and passive rest in physiological recovery after high-intensity exercises. Biology of Exercise, 9(1).
Jafari, R. A. (2021). Responses of blood lactate concentration, heart rate, and blood pressure using three active recovery methods versus passive recovery after an exhaustive exercise in young elite wrestlers. Journal of Exercise and Health Science, 1(2), 35-54.
KAUFMAN, F. L., HUGHSON, R. L., & SCHAMAN, J. P. (1987). Effect of exercise on recovery blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 19(1), 17-20.
Laukkanen, J. A., Kurl, S., Salonen, R., Lakka, T. A., Rauramaa, R., & Salonen, J. T. (2004). Systolic blood pressure during recovery from exercise and the risk of acute myocardial infarction in middle-aged men. Hypertension, 44(6), 820-825.
https://indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijrss&volume=2&issue=2&article=013
Nathial, Mandeep Singh. A COMPARATIVE AND ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELF-ESTEEM AND JOB SATISFACTION IN ATHLETES AND NON ATHLETES. Journal of Advances in Social Science and Humanities, 2(10).https://doi.org/10.15520/jassh210123
Sahraei, F., Khoshnam, E., & Nikseresht, A. (2013). Effect of active and passive recovery on blood pressure and heart rate in male athletes. Euro. J. Exp. Bio, 3(6), 335-8.
SINGH SIDHU, A., & SINGH, M. (2022). KINEMATICAL ANALYSIS OF HURDLE CLEARANCE TECHNIQUE IN 110M HURDLE RACE. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 4(2), 28–35. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/267
Singh, A., & Singh , D. M. (2013). PROMOTION OF RESEARCH CULTURE –ENHANCING QUALITY IN HIGHER EDUCATION. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 2(2), 202–208. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/152
SINGH, M., & SINGH SIDHU, A. (2016). A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BODY COMPOSITION AND RELATIVE HEALTH STATUS AMONG RESIDENT AND NON-RESIDENT STUDENTS IN DIFFERENT SCHOOLS OF J&K. International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, 5(3), 08–13. Retrieved from https://ijobsms.org/index.php/ijobsms/article/view/320
Singh, M., Kadhim, M.M., Turki Jalil, A. et al. A systematic review of the protective effects of silymarin/silibinin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cancer Cell Int 23, 88 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02936-4 https://cancerci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12935-023-02936-4
Copyright (c) 2024 Manoj Kumar Ahirvar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














