A CORRELATION STUDY OF RECOVERY INTERVENTION ON SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE
Abstract
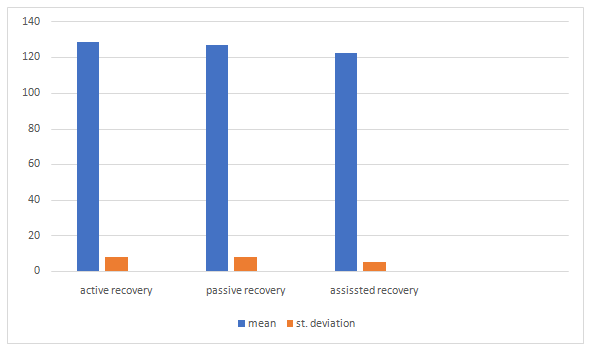
The current research study was to reveal the recovery treatment difference of active recovery, passive recovery and assisted recovery on systolic blood pressure. In this study there are total 54 subjects were taken (18 active recovery, 18 passive recovery and assisted recovery 18 male) all were national player of middle-distance runners from Bhopal SAI centre. Subjects’s age was between from 18 to 25 years. The research data were evaluated by blood pressure monitor. The accumulated data was analysed by evaluate the descriptive statistics to figure out standard deviation and mean among active, passive and assisted recovery on systolic blood pressure, and correlation Test. For assessment of Correlation, the level of significant was taken as 0.01 (2-tailed). Statistical evaluation was done by using statistical packages for social science (IBM SPSS 20 Version). As outcome the findings were that the correlation value is having negative relationship among active and assisted recovery (-0.596).Thus, the null hypothesis is failed to accept between active and passive recovery because no relationship occur among them but in case of active and assisted recovery there is a negative relationship which means assisted recovery is more suitable to back to normal systolic blood pressure as compare to active recovery because as active recovery and assisted recovery has inverse relationship and the mean value of assisted recovery method less as compare to other two recovery methods.
Downloads
References
Bogdanis, G. C., Nevill, M. E., Lakomy, H. K., Graham, C. M., & Louis, G. (1996). Effects of active recovery on power output during repeated maximal sprint cycling. European journal of applied physiology and occupational physiology, 74(5), 461-469.
De Oliveira, L. S., Fontes, A. M. G., Vitor, A. L. R., Vanderlei, F. M., Garner, D. M., & Valenti, V. E. (2020). Lower systolic blood pressure in normotensive subjects is related to better autonomic recovery following exercise. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1006.
Dimkpa, U., & Ugwu, A. C. (2010). Independent multiple correlates of post-exercise systolic blood pressure recovery in healthy adults. International journal of exercise science, 3(1), 25.
Ellis, K., Pothier, C. E., Blackstone, E. H., & Lauer, M. S. (2004). Is systolic blood pressure recovery after exercise a predictor of mortality?. American heart journal, 147(2), 287-292.
Jafari, R. A. (2021). Responses of blood lactate concentration, heart rate, and blood pressure using three active recovery methods versus passive recovery after an exhaustive exercise in young elite wrestlers. Journal of Exercise and Health Science, 1(2), 35-54.
Laukkanen, J. A., Willeit, P., Kurl, S., Mäkikallio, T. H., Savonen, K., Ronkainen, K., & Rauramaa, R. (2014). Elevated systolic blood pressure during recovery from exercise and the risk of sudden cardiac death. Journal of hypertension, 32(3), 659-666.
Laukkanen, J. A., Willeit, P., Kurl, S., Mäkikallio, T. H., Savonen, K., Ronkainen, K., & Rauramaa, R. (2014). Elevated systolic blood pressure during recovery from exercise and the risk of sudden cardiac death. Journal of hypertension, 32(3), 659-666.
Mandeep Singh Nathial, Analysis of set shot in basketball in relation with time to perform the course and displacement of center of gravity, American Journal of Sports Science, Vol.2 Issue.5 pp: 122-126 (2014). Retrieved from https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/paperinfo.aspx?journalid=155&doi=10.11648/j.ajss.20140205.
Mandeep Singh (2010). Evaluation And Improvement Of Sports Techniques Through Biomechanical Updated Analyzing Technology, University News, Journal of Higher Education Association of Indian Universities, Association of Indian Universities, Vol:48:Issue.05;2010 Pp45-57, 2010
Mandeep Singh Nathial, A Study of Adjustment and Emotional Intelligence of University Coaches in India,American Journal of Applied Psychology. Volume 3, Issue 6, November 2014 , pp. 122-126. doi: 10.11648/j.ajap.20140306.
Nathial, Mandeep Singh. A COMPARATIVE AND ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELF-ESTEEM AND JOB SATISFACTION IN ATHLETES AND NON ATHLETES.Journal of Advances in Social Science and Humanities,2(10).https://doi.org/10.15520/jassh210123
Singh, M., Kour, R., & Kour, A.,. A collaborative diversified investigation of respective responses of sports person coaches and organizations on criminalization of doping.International Journal of Health Sciences,6(S3), 11295–11310. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS3.8641
Roberts, L. A., Muthalib, M., Stanley, J., Lichtwark, G., Nosaka, K., Coombes, J. S., & Peake, J. M. (2015). Effects of cold water immersion and active recovery on hemodynamics and recovery of muscle strength following resistance exercise. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 309(4), R389-R398.
Copyright (c) 2024 Manoj Kunar Ahirvar, Minakshi Pathak

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














