COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DIFFERENT PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES BETWEEN THE STUDENTS OF TWO TYPES OF TRAINING INSTITUTION
Abstract
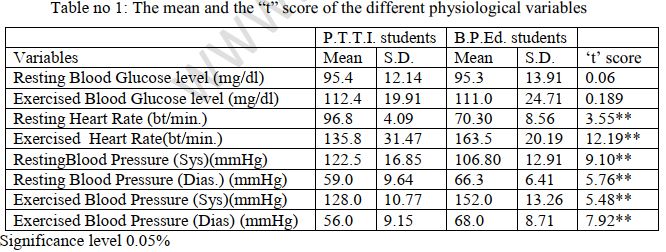
The purpose of the study was to find out the difference of the students of two type of training institution as the Bachelor of Physical Education and the primary Teachers Training institution considering different Physiological variables. 30 students at the age group of 21-25yrs. were considered from each of the institution as the subject of the study. The Physiological variables were blood glucose level, pulse rate, blood pressureand the data were collected both in the resting and exercised condition. There was no significant difference found in case of blood glucose level in both the resting and exercised condition. The resting heart rate(96.8) of the students of the P.T.T.I. were significantly higher but the exercised heart rate(135.8) were significantly lower than the students of the B.P.Ed. institution(70.30 and 163.5 respectively). The resting systolic blood pressure(122.5) of the P.T.T.I. students were significantly higher and the diastolic blood pressure(59.0) were significantly lesser than that of the B.P.Ed. students(106.80 and 66.3 respectively). In case of exercised condition both the systolic blood pressure(152.0) and the diastolic blood pressure(68) of the B.P.Ed. students were higher than that of P.T.T.I. students(128.0 and 56 respectively).
Downloads
References
2. Daniel, J., Oldridge, N., Nagle, F. and White, B. 1978. Differences and changes in VO2 max among young runners 10 to 18 years of age. Med Sci Sports, 10(3): 200-3. David, C. Nieman. Fitness and sports medicine a health related approach, physical activity and aging, III edition, Mayfield publishing company: California, p.429, 436.
3. Denti, L., Pasolini, G., Sanfelici, L., Benedetti, R., Cecchetti, A., Ceda, G.P., Ablondi, F., Valenti, G. 2000. Aging-Related Decline of Gonadal Function in Healthy Men: Correlation with Body Composition and Lipoproteins. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc., 48: 1.
4. Dixon EM, Kamath MV, McCartney N, Fallen EL. Neural regulation of the heart rate variability in endurance athletes and sedentary controls. Cardiovasc Res 1992; 26 (7): 713- 19.
5. Going, S., Williams, D., Lohman, T. 1995. Aging and body composition: biological changes and methodological issues. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev., 23: 411–58.
6. Guo, S.S., Zeller, C., Chumlea, W.C. and Siervogel, R.M. 1999. Aging, body composition, and lifestyle: the Fels Longitudinal Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 70(3): 405-411. 1999
7. Hawkins, S.A. Marcell, T..J., Victoria, J.S. and Wiswell, R.A. 2001. A longitudinal assessment of changes in VO2 max and maximal heart rate in master athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 33(10): 1744-50.
8. Krotkiewski, M., Bjorntorp, P., Sjostrom, L., Smith, U. 1983. Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose distribution. J. Clin. Invest., 72: 1150-1162.
9. Larsson, B., Svardsudd, K., Welin, L., Wilhelmsen, L., Bjorntorp, P., Tibblin, G. 1984. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow-up of participants in a study of men born in 1913. Br. Med. J., 288: 1401- 1404.
10. Najjar, M.F., Rowland, M. 1987Anthropometric reference data and prevalence of overweight, United States, 1976–80. Vital Health Stat. 11, 238: 1–73.