ANALYSIS OF BAD MOOD REGULATION STRATEGIES TO PERFORMANCE SATISFACTION AMONG MALE AND FEMALE COLLEGE ATHLETES
Abstract
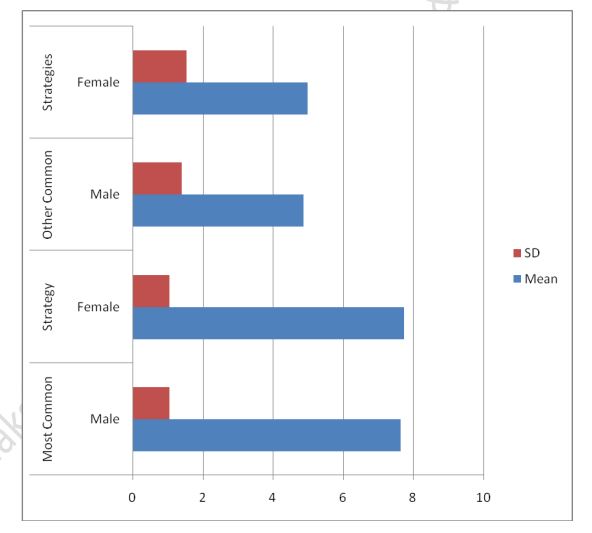
The purpose of the present study was to investigate the strategies that athletes use to regulate mood. Knowledge of the strategies that athletes use to regulate mood can help sport psychologists develop interventions designed to improve performance through controlling mood. The present study comprised of 310 athletes representing a range of different sports (e.g., badminton, hockey, karate, cricket, gymnastic, wrestling, basketball etc.). These participants were selected from different local colleges, universities and other institutions of higher education. All participants who have competed at national or state levels were included in the sample. The study investigated the strategies that college athletes use to regulate the mood dimensions of anger, confusion, depression, fatigue, tension, and vigor. Thus, the purpose of the present study was to investigate whether athletes use strategies common to all mood dimensions. In view of the above it is proposed to study the “Analysis of Bad Mood regulation strategies to performance satisfaction among male and female college athletes.
Downloads
References
Batson, C. D., Shaw, L. L., & Oleson, K. C. (1992). Differentiating affect, mood, and emotion: toward functionally based conceptual distinctions. In M. S. Clark (Ed.), Review of personality and social psychology: Emotion (pp. 294-326). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Beedie, C., Terry, P. C., & Lane, A. M. (2000). The Profile of Mood States and athletic performance: Two meta-analyses. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 12, 49-68.
Catanzaro, S.J. (2000). Mood Regulation and Suicidal Behavior. In T. Joiner & M. D. Rudd (Eds.) Suicide Science: Expanding the Boundaries (pp.81-103). Norwell, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Fazackerley, R., Lane, A.M., & Mahoney, C. (2004). Mood and performance relationships in wakeboarding. Journal of Sport Behavior, 27, 18-30.
Forgas, J. P. (1992). On bad mood and peculiar people: Affect and person typicality in impression formation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 62, 863-875.
Lane, A.M., & Levitt, P. (2002). The influence of depressed mood on other mood states and cohesion. Journal of Sports Sciences, 20, 67.
Martin, L. L. (2001). Mood as input: A configural view of mood effects. In Martin, L. L., & Clore, G. L. (Eds.), Theories of mood and cognition (pp 135-158). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.