DIAGNOSTIC STUDY OF VARIOUS PARAMETERS OF VITAL CAPACITY AMONG EXERCISERS AND NON EXERCISERS OF MIDDLE AGED MEN
Abstract
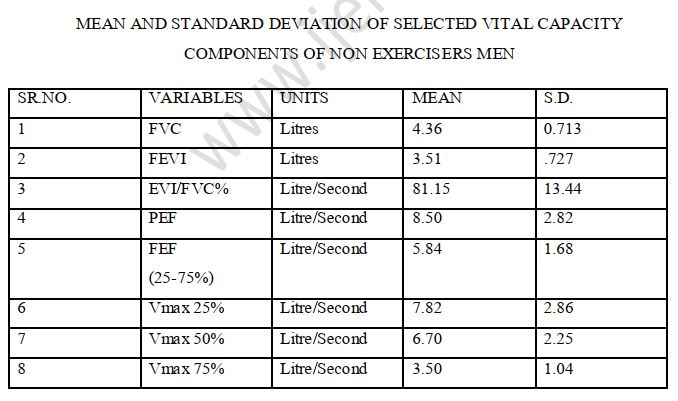
The purpose of the study was to analyse the comparison between vital capacity of exercisers and non exercisers male of middle aged men from various places of Punjab and Haryana. To determine this, 100 exercisers who were involved in any type of exercisers, regularly atleast for half an hour and 100 non exercisers who did not indulged in any type of exercise were randomly selected as subjects. To measure various selected variables of vital capacity i.e F.V.C(L), F.E.V1(L), FEV1/ FVC%(L/S), PEF(L/S), FEF(25-75%)L/S, Vmax25%, Vmax50%, Vmax75% spirometer was used. To analyse the computed scores of both the groups on vital capacity level, the‘t’ test was employed. Out of eight variables six variables showed significant differences. Following are the ‘t’ values of variables F.V.C(L) 4.02, F.E.V1(L) 4.74, PEF(L/S) 2.87, FEF(25-75%)L/S 2.79, Vmax25% 2.91, Vmax50% 2.79, which were found significant at .05 level but the ‘t’ test values of FEV1/ FVC%(L/S) and Vmax75% were 1.87 and 1.85 respectively and no significant difference was found.
Downloads
References
Ashley, F., W.B. Kannel, P.D. Sorlie, & R. Masson (1975) “Pulmonary function: Relation to aging, cigarette habit and mortality”, The Framingham study. Annals of Internal medicine 82: 739-745.
Astrand P.O.L (1963) “Girl Swimmers”, Acta Paediat Scand Suppl. 1.47:3-75.
Astrand, I. (1960): “Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age”, Acta physiological Scandinavica (suppl. 169). 1-92.
Astrand P.O (1952): Experimental studies of physical working capacity in relation to sex and age”, Copenhagen: Munksgard.
Bachman, J.C and Harvath, S.M. (1968): “Pulmonary function changes which accompany athletic training programmes”, Reseach Quarterly 39:235-242.
Bellman M.J & Mittman C. (1980): “Ventilatory muscle training improves exercise capacity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients”, American review of respiratory discussion, 121: 273-280.
Berglund, E., G. Birath, J. Bjure, G. Armby. I.Kjellmer, L. Sandqvist, & B. Soderhol (1963): “Spirometric stidies in normal subjects”‟ I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Medica Scandinavica. 173: 185-206 (1963).
Cerny, (1987): “Breathing pattern during exercises in Young Black and Caucasian subjects”, Journal of applied physiology, 62(6), 2220-23.
Dempsey J. &Seals D.R (1995): Aging, exercise and cardio pulmonary function”, In perspectives in exercise science and sports medicine: volume 8 exercise in older adults, edited by D.R. Lamb, C.V Gisolfi and E. Nadel (Carmel in USA: Cooper Publishing Group), pp. 237-304.
Ericsson, P., & L. Irnell (1974): “Spirometric studies of ventilator capacity in elderly people”, in J.R. Edge, K.K. Pump, J. Arias-Stella, Aging Lung: Normal Function. New York: MSS Information Corporation, 209-222.
Grimby G. & Soderholm B (1963): “Spirometric studies in normal subjects”, Acta Medical Scandinavica, 173: 199-206.
Jain, S.K, & C.K. Gupta(1974a): “Age, height and body weights as determinants of ventilator „norms‟in healthy men above 40 years of age”‟ In J.R. Edge, K.K. Pump, J. Arias-Stella, Aging Lung: Normal Function. New York: MSS Information Corporation, 190-202.
Johnson, B.D. & J.A. Dympsey (1991): “Demand vs. Capacity in the again pulmonary system”, In J.O. Holloszy (ed.),Exercise and sports sciences reviews. 19:171-210.
Kenney, R.A. (1982): Physiology of Aging: a synopsis Chicago”, year book medical publishers. Shepard R.J (1978): “Physical activity and Aging”, Chicago. Year book Medical Publishers, 40- 44, 85-95.
Slonum, N.B., & L.H. Hamilton (1976): “Respiratory Physiology”, (3rd Edition). St. Louis: Mosby.