AN EVALUATION OF TIME MOVEMENT ANTICIPATION AMONG FEMALE ATHLETES OF VARIOUS SPORTS
Abstract
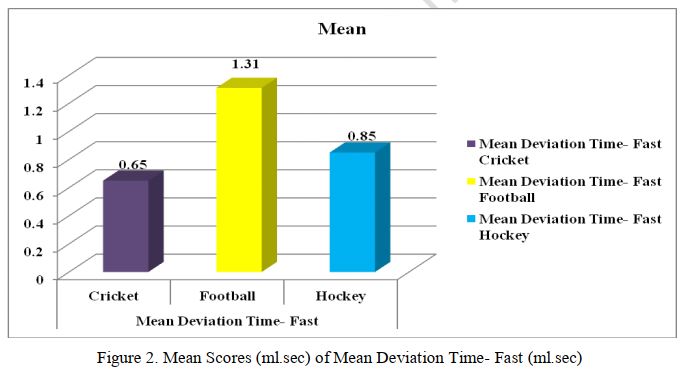
Anticipation in sport is the ability of the athlete to make decisions and to act ahead of time (Surkov, 1982). (Taylor 2016) noted that expert advantage in utilising informative cues for anticipation remains stable across sports, the cues that are most important or relevant for effective anticipation varies depending on the type of sport. Zhu ( 2012) mentioned that there is great potential in using technology-based assessment to overcome the limitations of traditional measurement methods. The Vienna Test System (VTS) developed by Schuh-fried GmbH (Moedling, Austria) is one such computerized system that is able to analyse many different sport psychology-related constructs. ZBA (Time/ Movement Anticipation Test) that measures time and movement anticipation ability, in which a green ball moves at a certain trajectory and suddenly disappears after a while. Participants are required to indicate where the ball hits the target line and the point on the target line where the ball will pass. The present study focused of highlighting possible differences in time and movement anticipation of visual stimuli movement. For this 45 university female athletes aged between 19 to 24 years with a mean and SD of 22.73± 2.14 of various sports (i.e. cricket, football and hockey; N=15 from each), ZBA was measured for mean deviation time (MDT)-slow and mean deviation time (MDT)-fast. ANOVA results revealed no significant difference among female athletes of different sports when considered on the score of MDT-slow (F(2,42)= 2.99, p= .061). But in MDT-fast significant differences was found (F(2,42)= 6.98, p= .002). Post-hoc test of Tukey HSD reveals significant difference in time movement anticipation between football and hockey group, also in football and cricket group.
Downloads
References
Taylor, L. (2016). "Anticipation skill in sport." Retrieved 11 February, 2017, from http://believeperform.com/performance/anticipation-skill-in-sport/.
Baumeister, R. F., Vohs, K. D., & Funder, D. C. (2007). Psychology as the science of selfreports and finger movements: Whatever happened to actual behavior? Perspectives on Psychological Science, 2, 396–403. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6916.2007.00051.x behavior research. Journal of Business and Psychology, 17, 245–260. doi:10.1023/A:10196376
Carolien H. (2002) “The smallest momentum possible” retrieved september 13, 2015 from http://www.du.ahk.nl/people/carolien/papers/reactiontime.htm, retrieved
Doğan B. (2009). Multiple-choice reaction and visual perception in female and male elite athletes. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 49 (1): 91-6.
Donaldson, S. I., & Grant-Vallone, E. J. (2002). Understanding self-report bias in organizational
Koçak S. (2010). Coincidence-anticipation timing and reaction time in youth tennis and table tennis players. Perceptual Motor Skills, 110 (3 Pt 1): 879-87.
Largo, R.H, Fischer, J.E., & Rousson V. (2003). Neuromotor development from kindergarten age to adolescence: development course and variability. Swiss Medical Weekly 133(13-14) retrieved on October 28, 2015 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.go /pubmed/12811675
Mangal S. K. (2007). Essentials of Educational Psychology. PHI learning private limited: New Delhi.
Schuhfried, G. (2013). Vienna test system: Psychological assessment. Moedling: Schuhfried.
Sport psychological ability and personality assessment with the Vienna Test System SPORT. (2014). Retrieved October 21, 2014, from http://www.schuhfried.com/viennatestsystem10/vienna-testsystem
Tenenbaum, G., Eklund, R., & Kamata, A. (2012). Introduction to measurement in sport and exercise psychology. In G. Tenenbaum, R. Eklund, & A. Kamata (Eds.), Measurement in sport and exercise psychology (pp. 3–7). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.vts/vienna-test-systemsport/
Zhu, W. (2012). Measurement practice in sport and exercise psychology: A historical, comparative, and psychometric view. In G. Tenenbaum, R. Eklund, & A. Kamata (Eds.), Measurement in sport and exercise psychology (pp. 9–21). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.